FATE OF INSULIN
· It is a peptide, gets degraded in the GIT if given orally.
· Injected insulin metabolized primary in the liver and small extend in the kidney and muscles.
· Half of the Insulin enters the portal vein circulation.
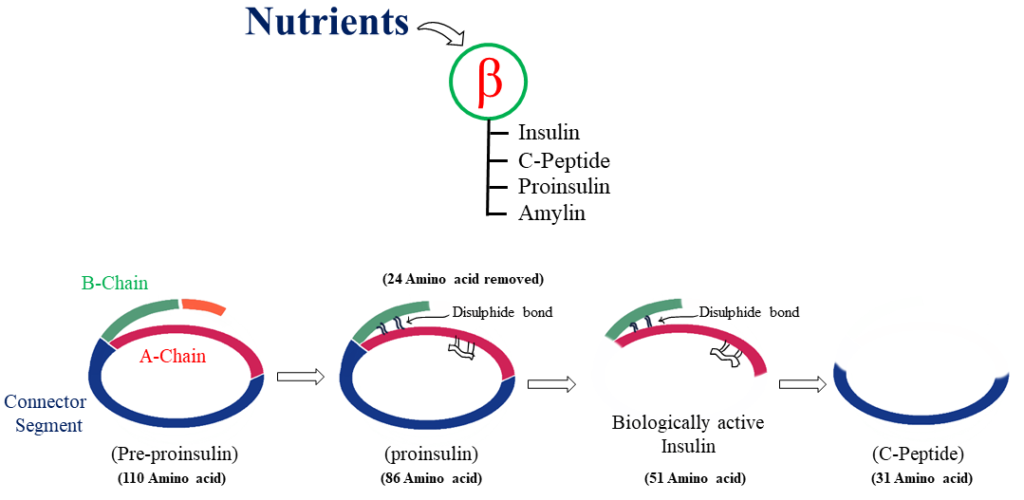
· During biotransformation A and B chains of the Insulin are separated and Disulphide bonds are reduced.
· Plasm t ½ is 5-9 minutes.
ADVERSE REACTION
· Hypoglycemia
· Weight gain
· Local injection site reaction
· Lipodystrophy (Abnormal distribution of fats)
INSULIN PREPARATION
1. Rapid and short acting Insulin preparation
· Regular Insulin is a short acting, soluble, crystalline, zinc Insulin.
· Insulin lispro, Aspart, and glulisine are rapid acting Insulin.
· Peak level of Insulin lispro are 30-90 minutes.
· Rapid Insulin should be administered SC. 3 minutes before meal, whereas rapid acting Insulin are administered before 15 minutes.
2. Intermediate acting
· Neutral protamine hagedorn (NPH)
· Administered AC. → Not i.v.
3. Long acting
· The iso-electric point of insulin glargine is lower than that of human Insulin, leading to formation of precipitate at the injection site that release over an extended period.
· Slower onset of action than NPH
4. Insulin combination
· Human Insulin: 70% NPH Insulin + 30% regular Insulin OR 50% of each.


Im very pleased to find this site. I need to to thank you for ones time for this particularly fantastic read!! I definitely really liked every part of it and I have you bookmarked to see new information on your site.
I need to to thank you for this good read!! I certainly enjoyed every bit of it. I have you saved as a favorite to look at new things you postÖ