BIOASSAY
- Bio-living, assay-test
- It is the process of determining the potency of the drug by using a suitable biological system like animals, tissues, microbes, etc.
PRINCIPLE OF BIOASSAY
- To compare the test substance with the International Standard preparation (IP, BP, USP) of the same.
- To find out how much test substance is required to produce the same biological effect as produced by the standard.
APPLICATION
- To determine the potency of a drug.
- To determine the dose of a drug required to produce a therapeutic or toxic response (ED50, LD50).
- This process is used in the development of new molecules or their preparation.
CHARACTERISTICS OF A GOOD ASSAY METHOD
- Sensitivity
- Specificity
- Repeatability
- Reproducibility
- Precision
- Accuracy
- Stability—tissue has to stay “bioassay-fit.”
BIOASSAY CAN BE PERFORMED ON:
- In-vivo → Intact animal
- In vitro → isolated tissues, specific cells, organisms.
- WHOLE ANIMALS
- Nor Adrenaline – Spinal Cat
- Cardiac Glycosides – Guinea Pig
- Insulin—Mice
- Estrogens—Ovariectomized Female Rat
- MICROORGANISMS
- Vit B12 – Euglena gracilis
- Tetracycline – Bacillus pumilus
- ISOLATED TISSUE
- Acetylcholine
- – Frog Rectus Abdominus muscle
- Histamine – Guinea Pig Ileum
- Adrenaline—Rat uterus
- Oxytocin—Rat uterus oestrogen primed
- DISPERSED CELLS
- Plasma LH estimation by stimulation of testosterone synthesis – on isolated Leydig cells
TYPES OF BIOASSAY
- There are mainly two types of bioassays:
- Quantal assay
- Direct end point assay (DEPA)
- LD50 determination
- Graded assay
- Matching
- Bracketing
- Interpolation
- Multiple points
- Three-point
- Four-point
- Six-point
- Cumulative dose response
- Quantal assay
QUANTAL ASSAY
- The response is in the form of “all or none,” i.e., either no response or maximum response. Drugs producing a quantal effect can be bioassayed by the endpoint method.
- The threshold dose producing a predetermined effect is measured
- Comparison between the results of the standard and the test
- E.g., bioassay of digitalis in cats, insulin-induced hypoglycemic convulsions in rats.
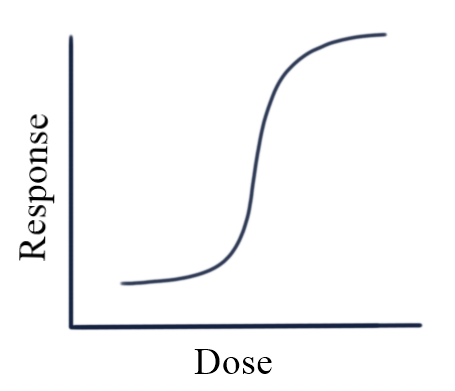
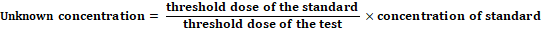
GRADED ASSAY
- The response is proportional to the dose, and the response may lie between no response and the maximum response.
MATCHING OR BRACKETING
- A constant dose of the standard is bracketed by varying doses of the test sample.
- until an exact matching between the response of the standard & that of the test sample is matched.
- The strength of unknown/test drug can be found by simple interpolation of bracketed response

ADVANTAGES
- Simple & faster method.
- The amount of test drug available is small
- Does not involve complicated calculations
- Does not depend on DRC
DISADVANTAGES
- less accurate
- Time-consuming
- Cannot get exact match of response
- Quantitative difference between the test & standard not obtained.
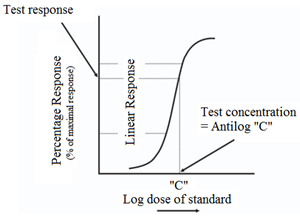
INTERPOLATION ASSAY
- The concentration of the test drug is interpolated from the dose-response curve graph (DRC).
- The DRC of the standard drug is plotted first, and then the different concentrations of the test drug are plotted.
- The dose of the test drug, which comes at the linear log dose-response relationship, is interpolated from the dose-response plot.

With a foundation in pharmacology, I am engaged in both teaching and research. My work has been published in reputed national and international journals, and I actively participate in scientific conferences to share findings and stay connected with emerging advancements. Thank you for visiting. Your interest is truly appreciated.
